Chlamydia & Gonorrhea Test
$69.00 Original price was: $69.00.$49.00Current price is: $49.00.
This at-home chlamydia and gonorrhea test is an easy and convenient way to test for two of the most common sexually transmitted infections. With a simple urine sample, you can get the results you need in just 1 to 3 business days. Take charge of your sexual health and get tested for STDs today.
Measures:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
Collection Method: Urine
Physician-Approved
All STD tests are reviewed and approved by third party independent physicians
Discreet & Confidential
Your test kit will be shipped in plain, unmarked packaging to ensure your privacy and confidentiality.
CLIA Certified
All tests performed in our CLIA certified laboratory using the same technology as hospital labs.
Test for chlamydia & gonorrhea from the comfort of home
Stay informed and protect your sexual health by testing for two of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs): chlamydia and gonorrhea. These bacterial infections often show no symptoms, making it easy to carry and unknowingly transmit them to others. With this at-home test, you can get the answers you need quickly, privately, and conveniently—right from the comfort of your home.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia, caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, is one of the most widespread STIs, particularly affecting young adults. It often shows no symptoms, so many people are unaware they’re infected. Without treatment, chlamydia can lead to serious long-term health complications. Thankfully, it’s easy to detect with a simple test, and it’s completely treatable with antibiotics. If you’re sexually active, getting tested regularly is a key part of taking care of your body and staying informed about your health.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, is another common STI that can also fly under the radar due to a lack of symptoms. Left untreated, gonorrhea can cause serious health problems, including infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease. It’s spread through unprotected sex, but like chlamydia, it’s entirely treatable once detected. The only way to know your status is through testing, and early detection makes treatment simple and effective.
Why Choose At-Home Testing?
Testing for STIs doesn’t need to be stressful. With this at-home kit, you can collect a simple urine sample in the comfort of your own home, and mail it back to our CLIA-certified lab using the prepaid envelope. Your results will be delivered securely to your private online account within a few days. It’s the easiest, most discreet way to stay on top of your sexual health—no appointments, no waiting rooms, just the information you need to stay healthy and informed. Whether you’re testing as part of your routine or have specific concerns, this test puts you in control.
Taking charge of your sexual health is an empowering step toward overall well-being, and the Chlamydia & Gonorrhea Test makes it easy to stay informed. Both chlamydia and gonorrhea are among the most common bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs), but they often fly under the radar with zero symptoms. This means you could be carrying an infection without even knowing it, which is why regular testing is so important.
Left untreated, these infections can lead to serious complications, including infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of contracting other STIs, such as HIV. Early detection is the key to preventing these long-term health consequences and stopping the spread to others.
This at-home test offers a discreet, convenient, and reliable way to know your status from the privacy of your own space. Whether you’ve had new or multiple partners, are experiencing symptoms, or simply want peace of mind, regular testing is a proactive way to protect your sexual health and well-being.
The ultimate at-home lab testing experience
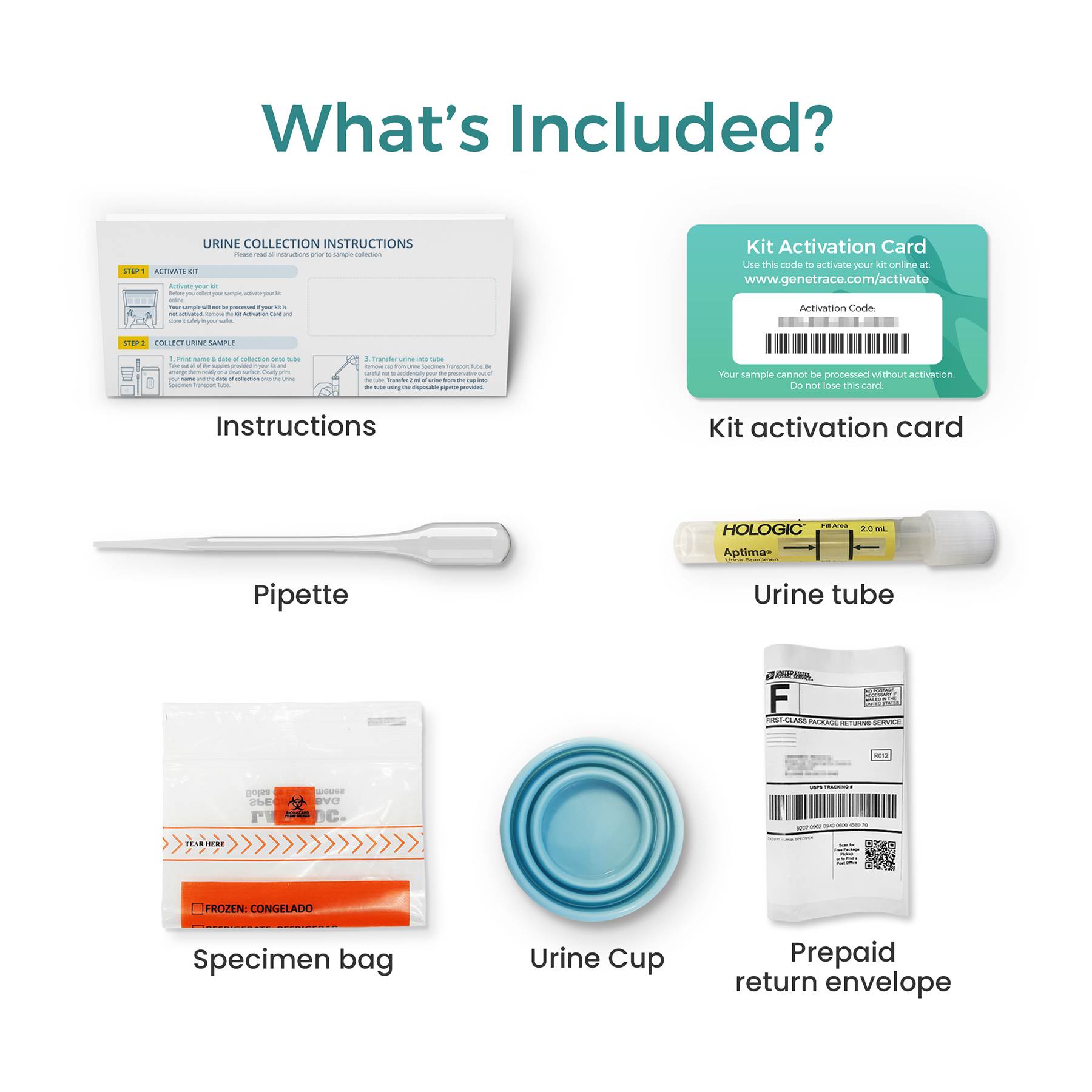
This convenient test kit includes everything you need to collect your sample and send it to the laboratory for quick and accurate results. All shipping and lab fees are included in the price, giving you a completely hassle-free experience. Get tested quickly and easily from the comfort of your own home.
Test for chlamydia & gonorrhea from the comfort of home
Stay informed and protect your sexual health by testing for two of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs): chlamydia and gonorrhea. These bacterial infections often show no symptoms, making it easy to carry and unknowingly transmit them to others. With this at-home test, you can get the answers you need quickly, privately, and conveniently—right from the comfort of your home.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia, caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, is one of the most widespread STIs, particularly affecting young adults. It often shows no symptoms, so many people are unaware they’re infected. Without treatment, chlamydia can lead to serious long-term health complications. Thankfully, it’s easy to detect with a simple test, and it’s completely treatable with antibiotics. If you’re sexually active, getting tested regularly is a key part of taking care of your body and staying informed about your health.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, is another common STI that can also fly under the radar due to a lack of symptoms. Left untreated, gonorrhea can cause serious health problems, including infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease. It’s spread through unprotected sex, but like chlamydia, it’s entirely treatable once detected. The only way to know your status is through testing, and early detection makes treatment simple and effective.
Why Choose At-Home Testing?
Testing for STIs doesn’t need to be stressful. With this at-home kit, you can collect a simple urine sample in the comfort of your own home, and mail it back to our CLIA-certified lab using the prepaid envelope. Your results will be delivered securely to your private online account within a few days. It’s the easiest, most discreet way to stay on top of your sexual health—no appointments, no waiting rooms, just the information you need to stay healthy and informed. Whether you’re testing as part of your routine or have specific concerns, this test puts you in control.
Taking charge of your sexual health is an empowering step toward overall well-being, and the Chlamydia & Gonorrhea Test makes it easy to stay informed. Both chlamydia and gonorrhea are among the most common bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs), but they often fly under the radar with zero symptoms. This means you could be carrying an infection without even knowing it, which is why regular testing is so important.
Left untreated, these infections can lead to serious complications, including infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of contracting other STIs, such as HIV. Early detection is the key to preventing these long-term health consequences and stopping the spread to others.
This at-home test offers a discreet, convenient, and reliable way to know your status from the privacy of your own space. Whether you’ve had new or multiple partners, are experiencing symptoms, or simply want peace of mind, regular testing is a proactive way to protect your sexual health and well-being.
The ultimate at-home lab testing experience
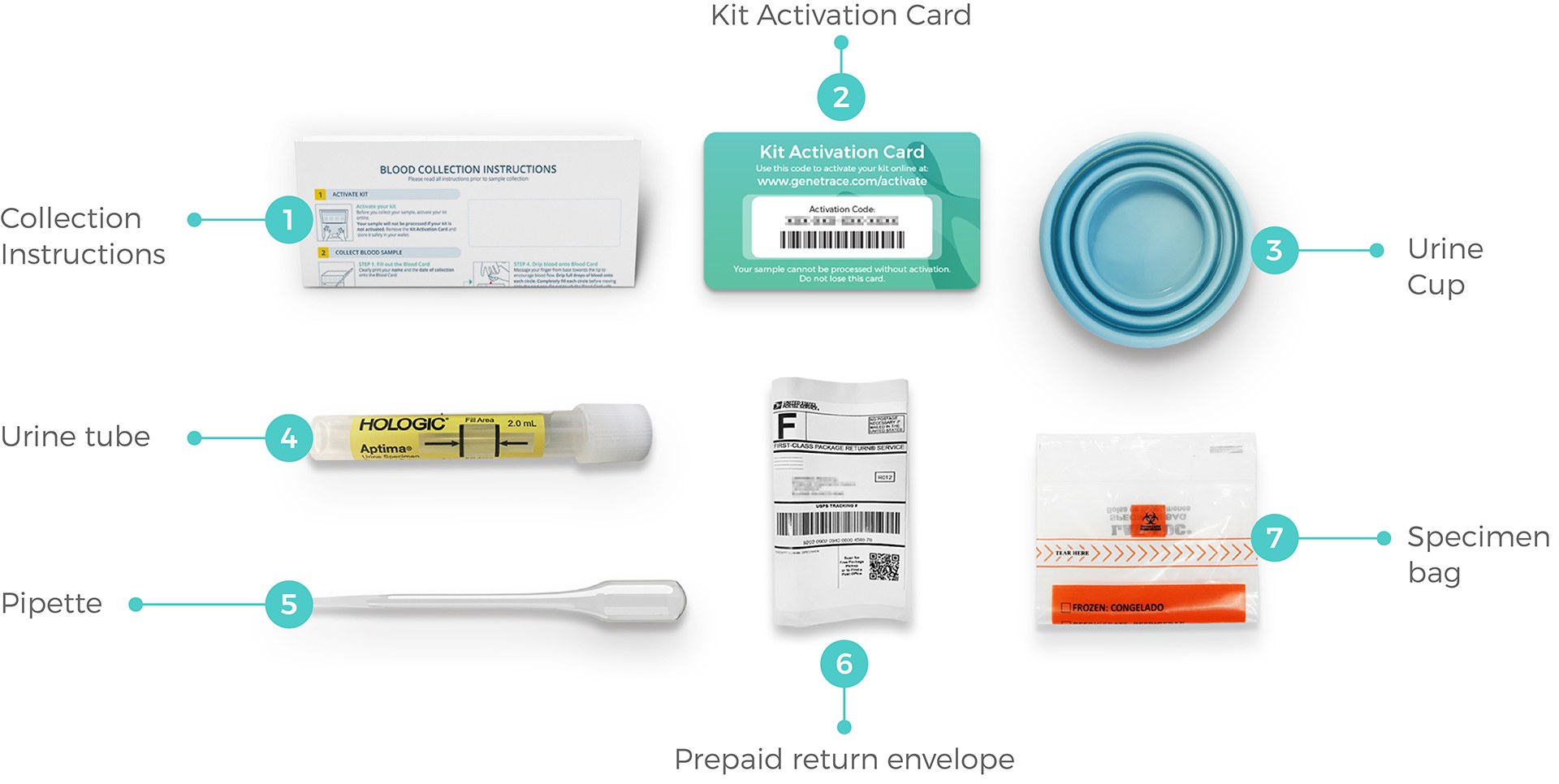
This convenient test kit includes everything you need to collect your sample and send it to the laboratory for quick and accurate results. All shipping and lab fees are included in the price, giving you a completely hassle-free experience. Get tested quickly and easily from the comfort of your own home.

Take control of your sexual health
Free Physician Consult
Private & Confidential
Discreet Packaging
HIPAA Compliant
Free Physician Consultation
Get a free telehealth consult with an independent physician if you receive a positive result.
Discreet Packaging
Your test kit will be sent in plain, unmarked packaging for your discretion and privacy.
Private & Confidential
Receive secure, confidential results through your online dashboard. We’ll keep you updated every step of the way.
HIPAA Compliant
We never share your data with any third-party without your express permission, ensuring that your personal information is safe and secure.
How it works
Purchase your kit
Activate your test at genetrace.com using the activation code provided inside your kit.
Collect sample
Your test kit includes everything you need to collect a urine sample in the comfort and privacy of your own home.
Ship sample to the lab
No extra charges, no extra hassle – just mail it back in the prepaid envelope and we’ll take care of the rest.
Receive your results
Receive confidential results in your secure online portal within 1-3 business days after testing begins.
FAQ's
Here are the answers to the most frequently asked questions about this test.
The Chlamydia & Gonorrhea Test is your discreet, at-home solution for checking in on your sexual health. This test lets you screen for two of the most common STIs — chlamydia and gonorrhea — in the comfort and privacy of your own bathroom. No awkward clinic visits, no waiting rooms, just quick results and peace of mind.
The test is simple and straightforward. Upon receiving your kit, you’ll use the included instructions to collect a small urine sample in the privacy of your home. You then seal the sample in the included collection container and mail it to our lab using the prepaid envelope. From there, the sample is processed in our CLIA-certified laboratory, and your results are ready in just 1-3 business days after the lab receives your sample.
If you are sexually active—especially if you’ve had unprotected sex, multiple partners, or new partners—you should consider regular testing for STIs. This is particularly important because both chlamydia and gonorrhea can be asymptomatic, meaning you or your partner could be infected without realizing it. Regular screening ensures early detection and treatment, contributing to your overall sexual health.
Sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea are incredibly common, particularly among young and sexually active individuals. However, many people infected with these STIs have zero symptoms, meaning you could carry the infection without knowing. Early detection means early treatment, preventing complications such as chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, or transmission to partners. Testing is a proactive way to protect your health and that of your partners.
The Chlamydia & Gonorrhea Test offers the same high-quality testing you’d find at a clinic, but with the convenience of at-home collection. There’s no need to schedule an appointment, visit a doctor’s office, or wait in a clinic. The entire process is designed to be discreet, affordable, and convenient—putting you in control of your sexual health.
The all-in-one home test
Related Products
$99.00 Original price was: $99.00.$79.00Current price is: $79.00.